Encoding and decoding flat files in Azure Logic Apps workflows using Text and XML formats
Encoding and decoding flat files, as well as converting between text and XML formats, is a common requirement in Azure Logic Apps workflows, especially for integrating with legacy systems or processing EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) files. Below is a detailed guide on how to achieve this using Azure Logic Apps and an Integration Account.
Prerequisites
- Azure Logic Apps: Create a Logic App in the Azure portal.
- Integration Account: Required for encoding/decoding flat files and XML. Create an Integration Account in the Azure portal and link it to your Logic App.
- Schemas: Define schemas for your flat files (e.g., CSV, fixed-width) and XML files using the Enterprise Integration Pack (EIP).
Steps to Encode and Decode XML
A. Decode XML (Convert XML to Text or JSON)
- Upload XML Schema to Integration Account:
- Go to your Integration Account in the Azure portal.
- Under Settings, select Schemas.
- Click Add and upload your XML schema- XSD file (Sample schema file) and MAP- XSLT file (Sample xslt file).
- Add a Trigger to Your Logic App:
- Use a trigger like When a file is added to a blob storage or HTTP Request to receive the XML file (Sample xml testing data).
- Add the “XML Validation” Action:
- In your Logic App, add a new action and search for XML Validation.
- Configure the action:
- Content: Select the XML content (e.g., from the trigger output).
- Schema Name: Select the schema you uploaded to the Integration Account.
- Output:
- The validated XML can be processed further or converted to JSON using the Parse JSON action.
B. Encode XML (Convert Text or JSON to XML)
- Prepare JSON or Text Data:
- Use actions like Compose or Parse JSON to generate or format the JSON/text data that matches your XML schema.
- Add the “XML Transformation” Action:
- Add a new action and search for Transform XML.
- Configure the action:
- Content: Select the JSON/text content to transform.
- Map: Select the map (XSLT file) you uploaded to the Integration Account.
- Output:
- The output of the Transform XML action will be the XML file.
Here's how Logic Apps should look:
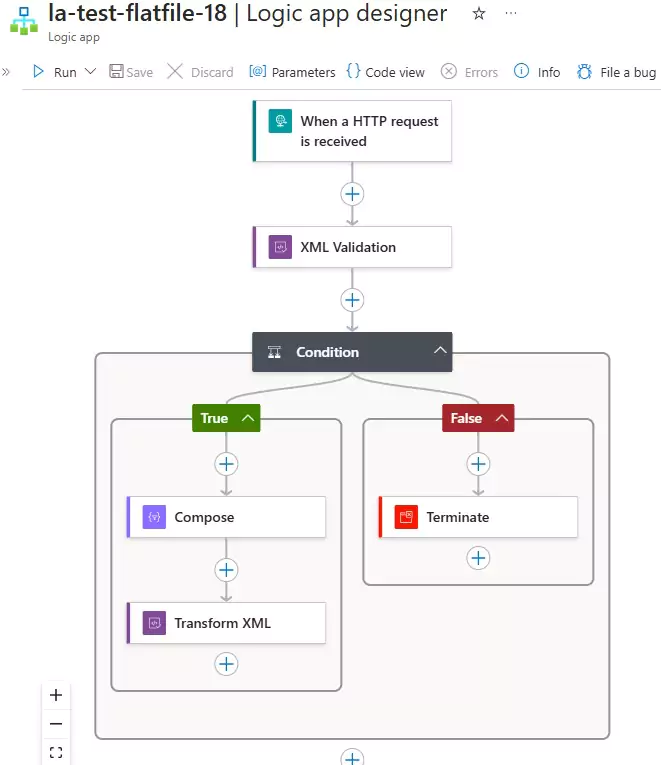
You can download the logic app template from the estudy247 GitHub repository – la-test-flatfile-18
Steps to Encode and Decode Flat Files and XML
A. Encode a Flat File (Convert Flat File to XML or JSON)
- Upload Flat File Schema to Integration Account:
- Go to your Integration Account in the Azure portal.
- Under Settings, select Schemas.
- Click Add and upload your flat file schema- XSD file (Sample schema file)
- . You can create this schema using tools like Visual Studio or Azure Logic Apps Designer.
- Add a Trigger to Your Logic App:
- Use a trigger like When a file is added to a blob storage or HTTP Request to receive the flat file (Sample xml testing data).
- Add the “Flat File Encoding” Action:
- Add a new action and search for Flat File Encoding.
- Configure the action:
- Content: Select the XML/JSON content to encode.
- Schema Name: Select the schema you uploaded to the Integration Account.
- Output:
- The output of the Flat File Encoding action will be the flat file in text format.
B. Decode a Flat File (Convert XML or JSON to Flat File)
- Prepare XML or JSON Data:
- Use actions like Compose or Parse JSON to generate or format the XML/JSON data that matches your flat file schema.
- Add the “Flat File Decoding” Action:
- In your Logic App, add a new action and search for Flat File Decoding.
- Configure the action:
- Content: Select the flat file content (e.g., from the trigger output).
- Schema Name: Select the schema you uploaded to the Integration Account.
- Output:
- The output of the Flat File Decoding action will be in XML or JSON format, depending on your schema.
Here's how Logic Apps should look:
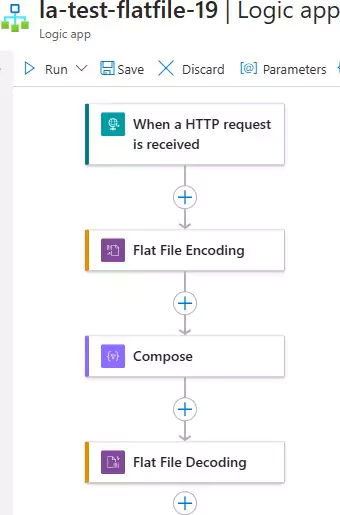
You can download the logic app template from the estudy247 GitHub repository – la-test-flatfile-19
Tools for Creating Schemas and Maps
- Visual Studio: Use the BizTalk Schema Editor to create XSD schemas for flat files and XML.
- Azure Logic Apps Designer: Use the schema editor in the Azure portal (limited functionality).
Best Practices
- Validate Schemas: Test your schemas thoroughly to ensure they match the expected file format.
- Error Handling: Add error handling steps (e.g., Scope and Condition actions) to manage invalid files or encoding/decoding failures.
- Logging: Use Azure Monitor or Log Analytics to track workflow execution and troubleshoot issues.
