Invoke REST API endpoints within workflows using Azure Logic Apps
Calling REST API endpoints from workflows in Azure Logic Apps is a common use case. You can use the HTTP or HTTP + Swagger actions to interact with REST APIs. Below is a detailed guide and example of how to use the HTTP action to call a REST API and handle the response.
Steps to Call a REST API Endpoint Using HTTP Request and Response
- Add a Trigger:
- Start your Logic App with a trigger. For example:
- Use the HTTP Request trigger if you want to trigger the workflow via an external HTTP request.
- Use a Recurrence trigger if you want to run the workflow on a schedule.
- Start your Logic App with a trigger. For example:
- Add an HTTP Action:
- In the Logic App Designer, click on + New Step.
- Search for and select the HTTP action.
- Configure the HTTP Action:
- Method: Choose the HTTP method (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- URI: Enter the REST API endpoint URL.
- Headers: Add any required headers (e.g.,
Content-Type,Authorization). - Body: If the method requires a body (e.g., POST or PUT), provide the JSON payload.
- Handle the Response:
- Use the output of the HTTP action to process the response (e.g., parse JSON, store data, or send a response back).
- Return a Response (Optional):
- If your workflow is triggered by an HTTP request, you can use the Response action to send a response back to the caller.
Example: Call a REST API and Return the Response
Scenario:
You want to create a Logic App that:
- Accepts an HTTP request with a city name.
- Calls a weather API to get the current weather for that city.
- Returns the weather data as an HTTP response.
Steps in Logic App Designer
- Trigger:
When an HTTP request is received- This trigger allows the Logic App to be invoked via an HTTP POST request.
- Add a sample JSON schema to define the expected input:
{ "type": "object", "properties": { "city": { "type": "string" } } }
- Action:
HTTP- Add an HTTP action to call the weather API.
- Method:
GET - URI:
https://api.weatherapi.com/v1/current.json?key=YOUR_API_KEY&q=@{triggerBody()?['city']}- Use dynamic content
@{triggerBody()?['city']}to pass the city name from the trigger.
- Use dynamic content
- Headers: None (unless the API requires authentication).
- Method:
- Add an HTTP action to call the weather API.
- Action:
Response- Add a Response action to return the weather data to the caller.
- Status Code:
200 - Headers:
Content-Type:application/json
- Body: Use the
Bodyoutput from the HTTP action to return the weather API response.
- Status Code:
- Add a Response action to return the weather data to the caller.
Here's how Logic Apps should look:
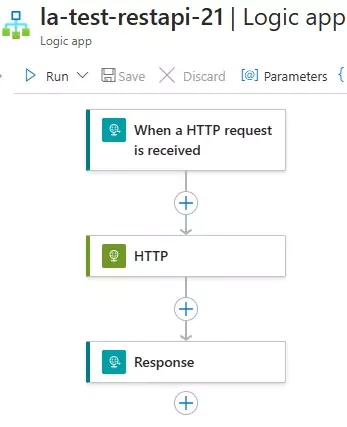
Testing the Workflow
- Save and Run the Logic App.
- Use a tool like Postman or cURL to send an HTTP POST request to the Logic App’s HTTP trigger URL.
- Example request body:
{ "city": "London" }
- Example request body:
- The Logic App will:
- Call the weather API for the specified city.
- Return the weather data as the HTTP response.
You can download the logic app template from the estudy247 GitHub repository – la-test-restapi-21
Key Notes:
- Dynamic Content: Use dynamic content (e.g.,
@{triggerBody()?['city']}) to pass data between steps. - Error Handling: Use the Configure run after settings to handle errors (e.g., retry or return an error response).
- Authentication: If the API requires authentication, configure the headers or use a managed identity.
This approach allows you to create flexible and powerful workflows that interact with REST APIs and return responses to clients.
